By Dhananath Fernando
The appointment of cabinet ministers and state ministers is still a topic at dinner tables, especially on the state ministerial portfolios. This is mostly because specific industries or fields have been provided for state ministers. There is general criticism surrounding ministers being appointed to micro sectors of the industries while the general expectation from a minister is to serve a broader mandate, and do justice to taxpayers’ money by formulating and implementing policies.
Many critics question the role a minister could play in a comparatively small industry where the designing, production, marketing, and distribution are mainly done by the micro-entrepreneurs themselves. For example, the state ministerial portfolio for Batik, Handloom Fabrics, and Local Apparel Products has been a topic of discussion since the appointments. Another state ministry that is being widely discussed is that of Cane, Brass, Clay Furniture, and Rural Industry Promotion.
The counterargument is that previous state minister portfolios were just token positions with no decision-making power. It is argued that in this case, ministers have been provided a specific role, scope, and focus, and people can directly hold them accountable for their industries and industry-related concerns. At the same time, a measurable key performance indicator (KPI) can be easily implemented and the respective and relevant institutions can be assigned to each minister. According to a recent TV interview by President’s Secretary Dr. P.B. Jayasundera, state ministers and their teams led by the ministry secretary have been given the decision-making power in that respective industry. According to Dr. Jayasundera, it is a scientific way of structuring and utilising taxpayer money without just appointing state ministers for the sake of doing so.
I believe there is truth to both arguments on the method of assigning the ministerial portfolio. The ground-level reality is that most of these assigned domestic industries are run by micro, small, and medium entrepreneurs (MSMEs) or businessmen who represent the private sector. It is important to remember that these small businesses are still part of the private sector and not the Government. The Government’s role is more to regulate some industries and facilitate the business processes because micro and small enterprises have industry-specific challenges as well as common challenges in running their daily operations. The minister’s role is to work with these sectors and assist them with reducing regulatory barriers for the sector to perform to its full potential.
Common challenges
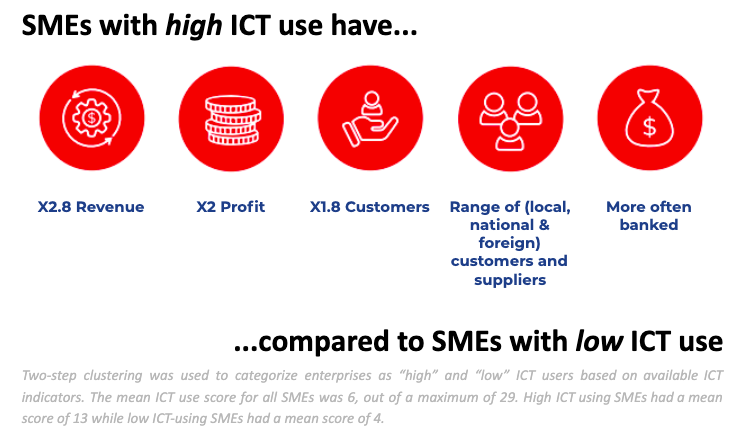
According to the Advocata Institute’s report “Barriers to Micro and Small Enterprises” in Sri Lanka, one main bottleneck across all industries is access to finance. Access to finance has multiple dimensions extending to the banking and financing sector, but it starts from the fundamental point of business registration.
Over the years, we have underestimated the potential of micro and small enterprises (leaving the medium enterprises aside). We have provided step-motherly treatment to the MSME industry to the extent of not even focusing on their ability to register their businesses.
According to the Advocata report, sole proprietorships comprise about 61% of total businesses in Sri Lanka and provide 27% of national employment. Interestingly, about 25% of the establishments are run by women and contribution from women-led enterprises increases up to 35% in rural areas.
While the whole country focuses on the big picture of revamping the entire domestic and specialised sectors such as batik, local apparels, handlooms, pottery, rattan, etc., our research has revealed that about 45% of micro-enterprises and 10% of small enterprises have not even obtained a basic business registration. The meaning of not having a business registration is that they do not have access to finance or any Government-sponsored programme or project.
Poor enthusiasm for business registration is mainly a result of the horrendous process of registering a proprietorship or partnership. A proprietorship or a partnership can be registered under the Business Names Ordinance Act No. 7 of 1987, which is under the authority of each provincial council and provides room for each provincial council to run their own procedure on registration of a proprietorship or partnership.
So even though a specific minister may have been given scope and specific task of revamping micro, small, and local enterprises, the minister may still face challenges due to common regulatory barriers starting from the business registration process, which is the entry ticket, to finance and markets, and even for relief schemes during Covid-19 brought in by the Government.
The good news is the Government and Department of Census and Statistics (DCS) have initiated an e- registry platform for registering micro and small enterprises. According to Advocata statistics, 97% of micro-businesses and 85% of small businesses are registered as sole proprietorships. This e-registration system is indeed a move in the right direction. Then, the authorities must also ensure that the e-registration process will be simple and not a replication where the same documents are just submitted online. A system of just submitting documents such as deeds, rent agreements, etc. online would add an additional burden for budding entrepreneurs; to scan and submit documents online in addition to the time they spend getting grama sevaka certificates, rent agreements, and a list of other documentation. Advocata has recommended the New Zealand model and a South Korean model where there is a three-step business registration process, while in Sri Lanka the current process has seven steps.
Daily survivors vs. entrepreneurs
Having a simplified business registration process is the first step of addressing the problem of access to finance and providing government assistance and accessing markets. Having a simple business registration process will ensure an effective tax collection system where businesses can grow and expand.
One other reason for the poor enthusiasm pertaining to registering a business is in the fear of paying taxes. As a result, most of these micro-businesses limit themselves to being “daily survivors” as opposed to them becoming real micro and small “entrepreneurs’’.
There is a significant difference between someone who just runs a small business for daily survival and someone who takes a risk in the form of money, property, time, or any form for entrepreneurship.
What Sri Lanka requires is for micro and small entrepreneurs to migrate from “daily survivors” to micro-entrepreneurs. The Government can facilitate the process by having a conducive environment for businesses, and the new state ministers can take this lead.
Industry-specific challenges
While the micro and small enterprises have been oppressed at the registration level, at the same time, there are industry-specific regulatory issues.
Most of these industries require a license for their sourcing and a license or a government authorisation that has to be taken at each touchpoint. In most industries, sourcing of raw material and transportation of raw materials both require licences. Some of the regulations are placed with good intentions, but most of it has ended up with extra bureaucracy burdening the industry and opening doors to corruption. All licences have just ended up being another hurdle for these entrepreneurs to cross. Additionally, these licences are also an opportunity for regulatory officials to earn extra money in the way of corruption and by providing preferential treatment to the affluent and higher classes of business that have networked with local political power centres.
The new industry-specific ministers’ primary mandate when developing these industries has to be a facilitatory role and not an interventionist role. The prosperity of micro and small enterprises will depend on this. The new ministers have to ensure that they do not apply the “brakes” by introducing more regulatory barriers; rather, they should remove those barriers in each sector for sustainable growth.
At the same time, they should not push the accelerator in the wrong direction to create market distortions which will impact other more productive sectors while bureaucratic powers work only thinking about their sector at the expense of others.
Sri Lankans are more than capable of competing at the global level and “daily surviving micro and small businesses” will jump to the seat of “micro and small entrepreneurs” if we facilitate and provide a more simple regulatory scheme.
We should never underestimate the common man’s skill and the ability of micro and small enterprises, which at present are already contributing more than 30% of our national employment.