Originally appeared in the Daily FT , Daily Mirror, Ceylon Today, Sunday Times and Ada Derana Business
New measures treating the symptoms rather than the disease.
COLOMBO, Sri Lanka— Harsh enforcement of price controls may worsen food shortages.
The Commissioner of Essential Services has been granted the power to seize food stocks held by traders and retailers and regulate prices.
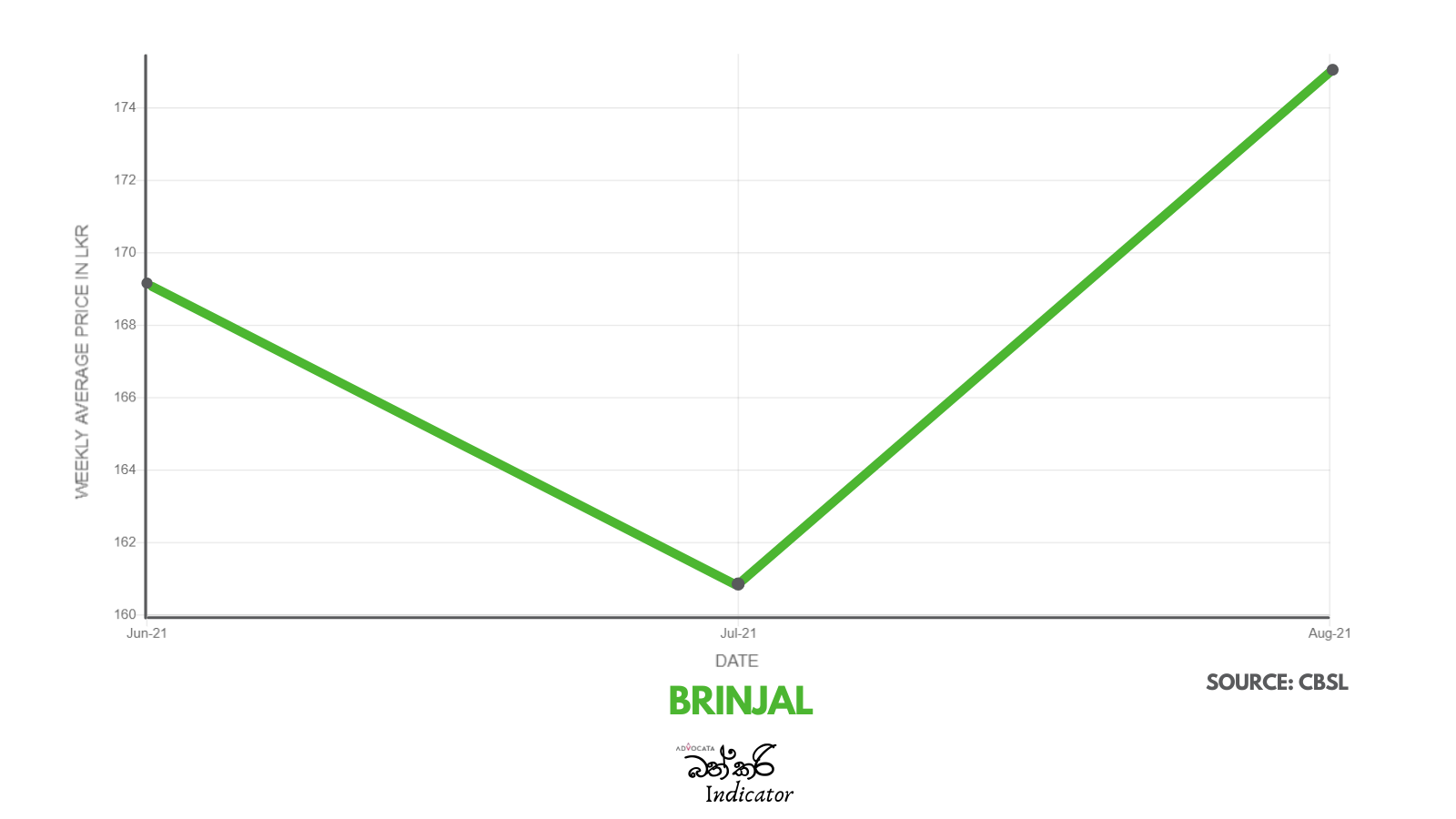
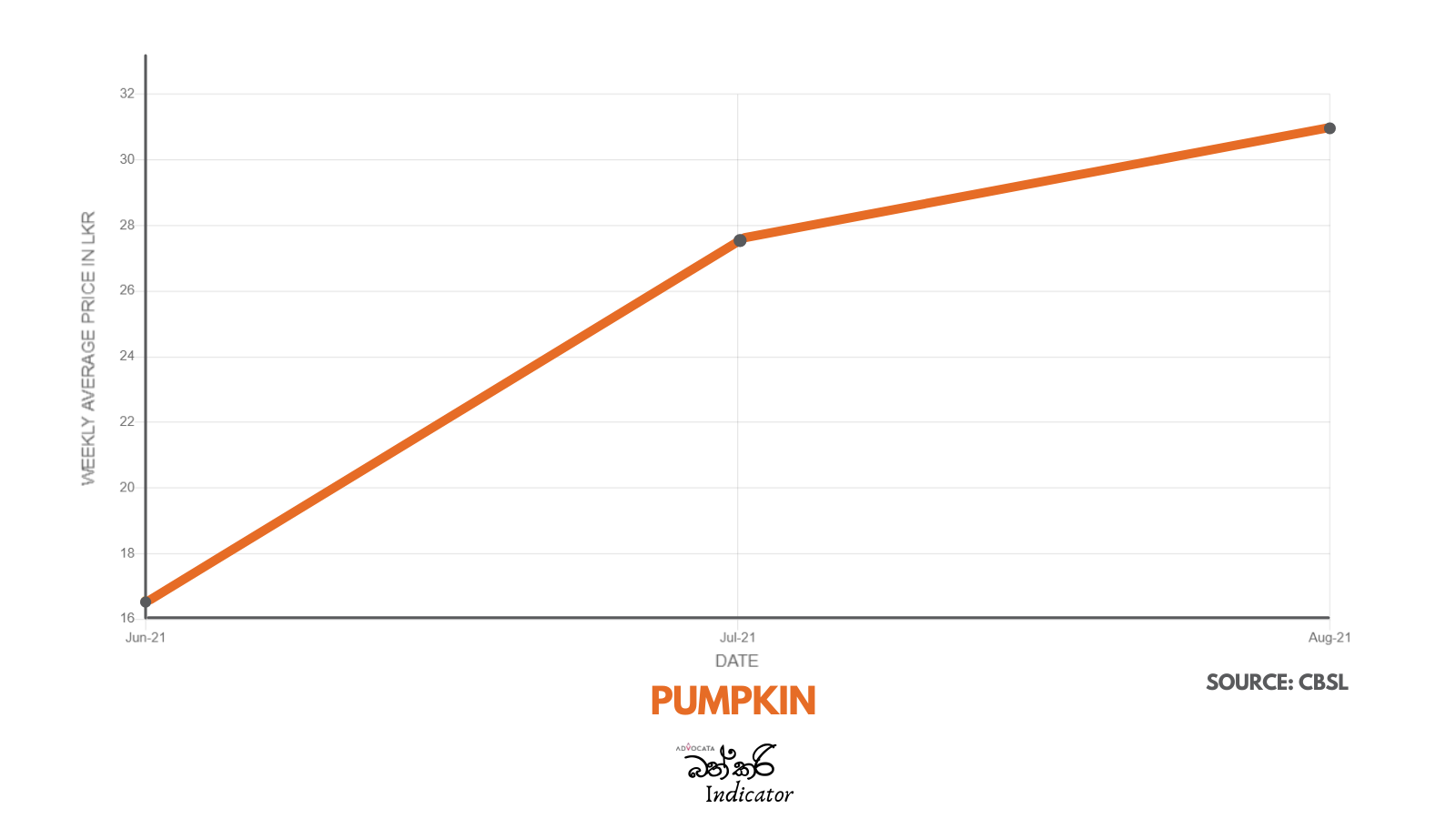
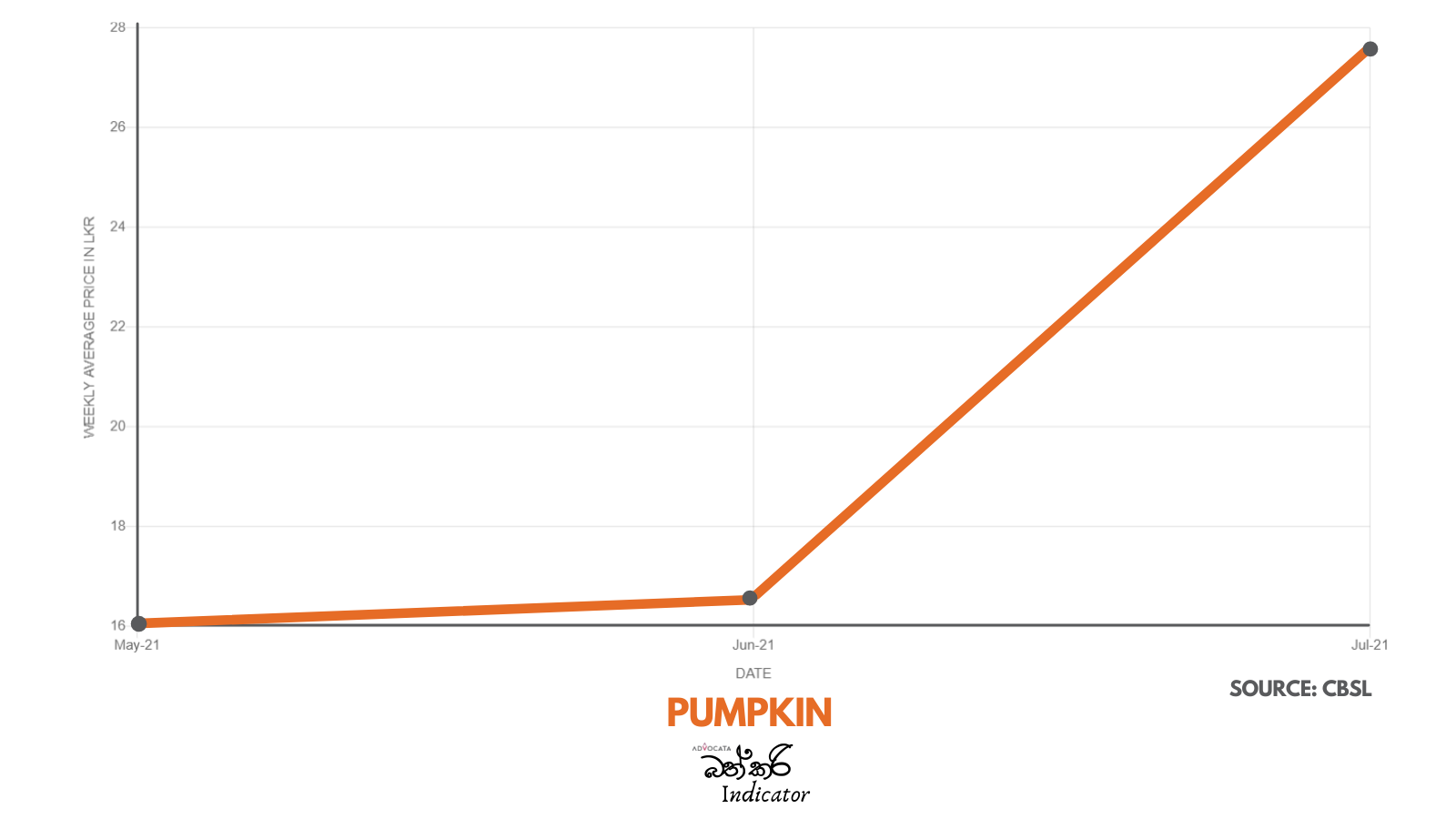
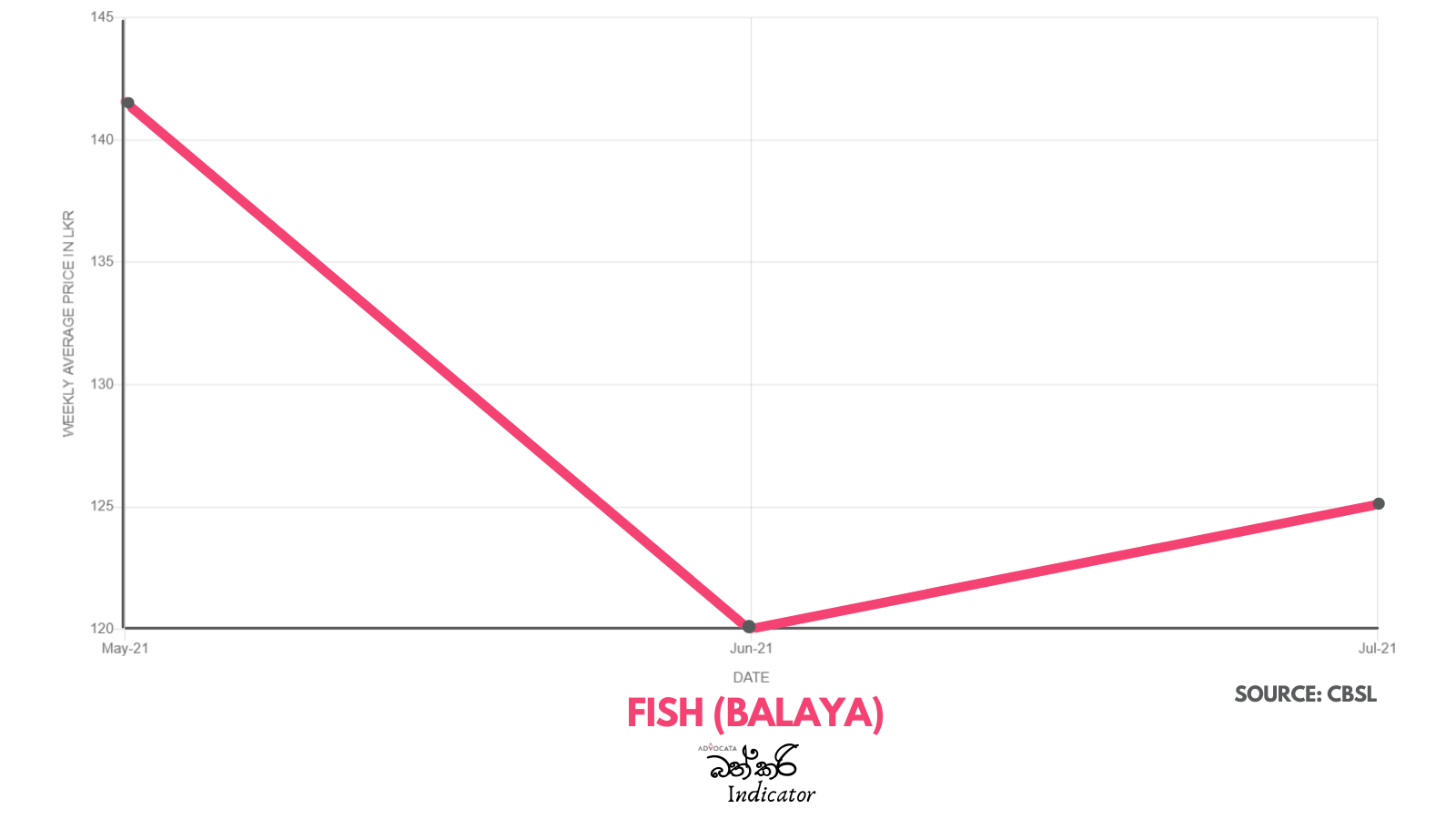
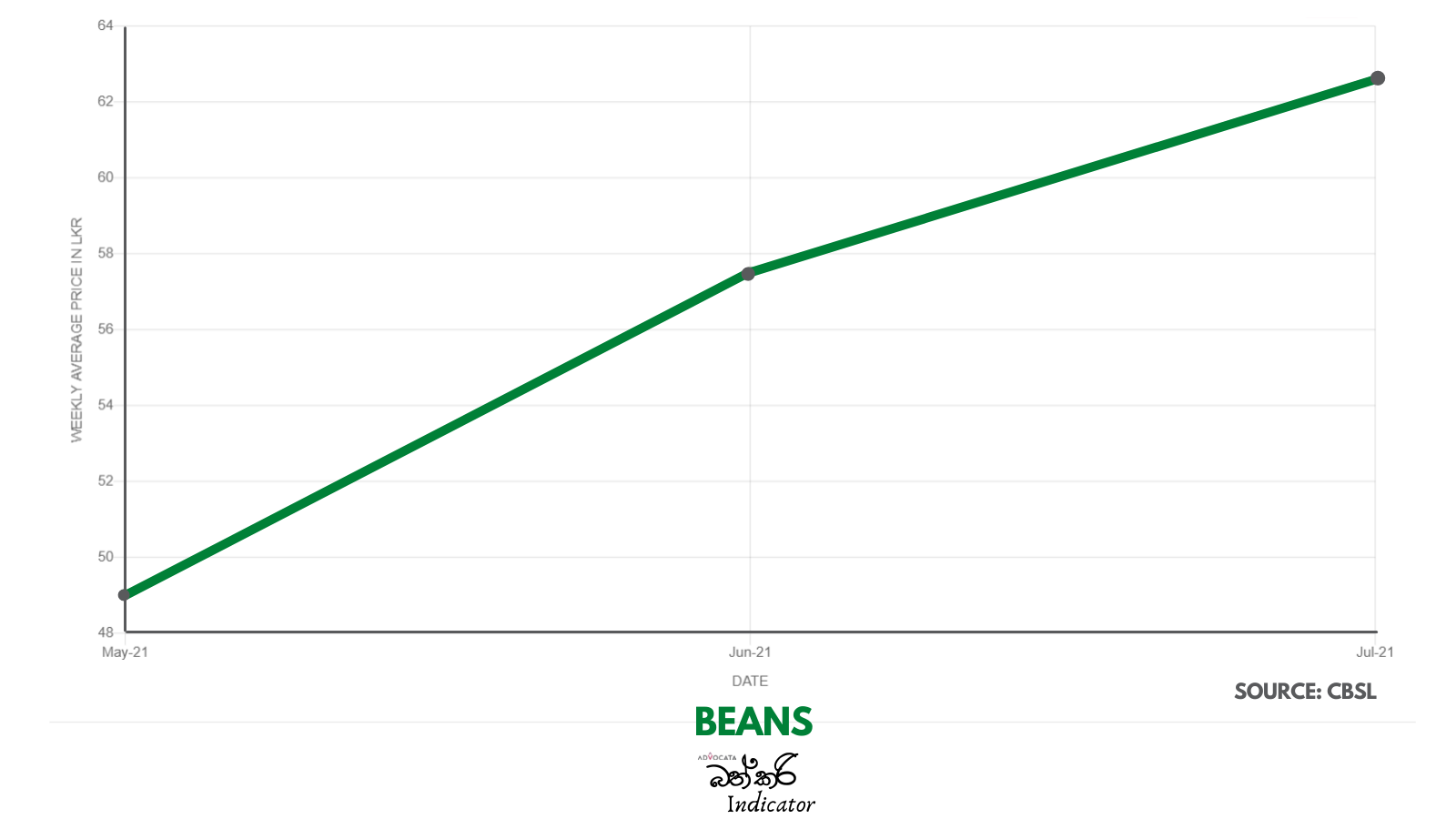
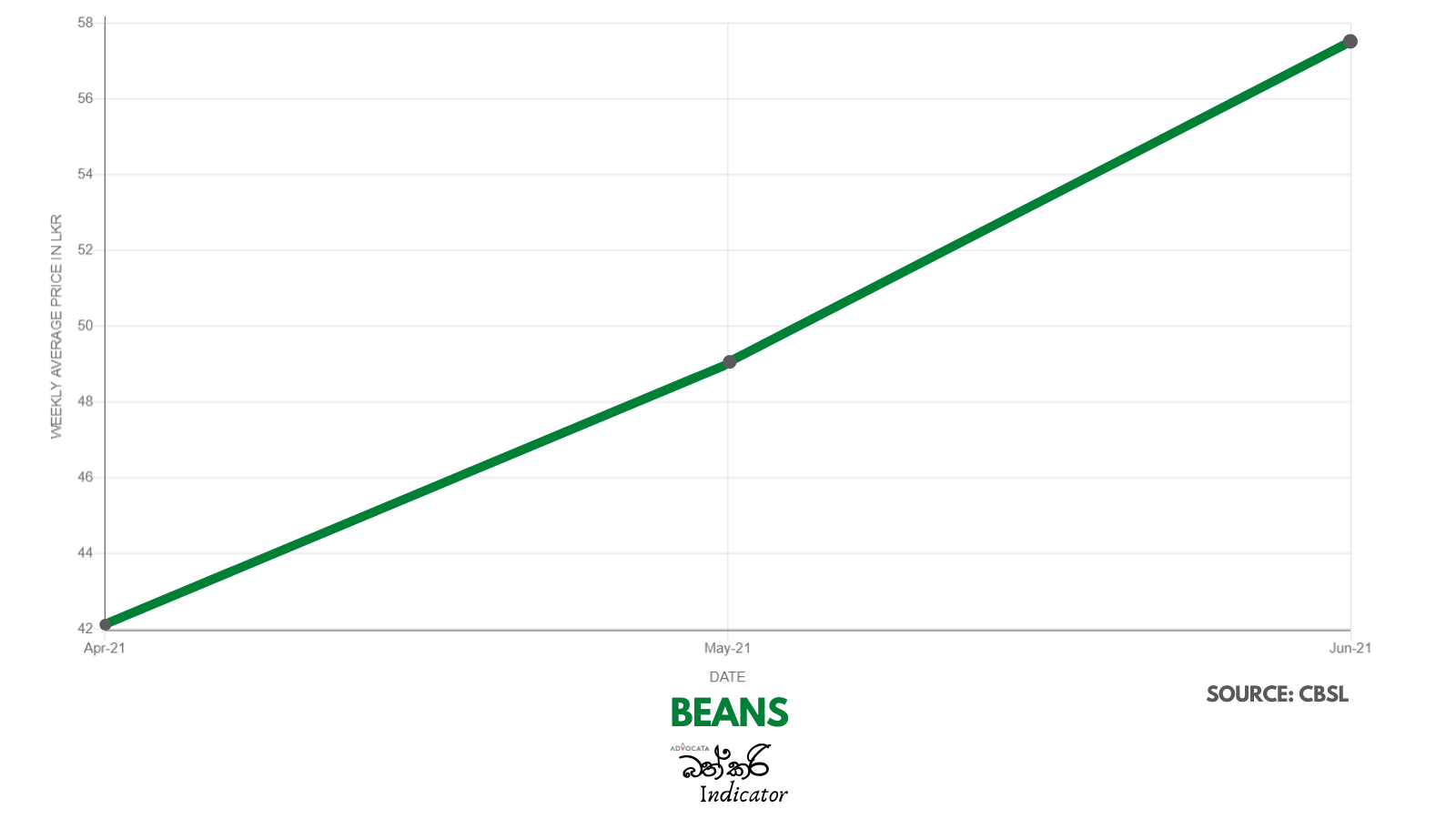
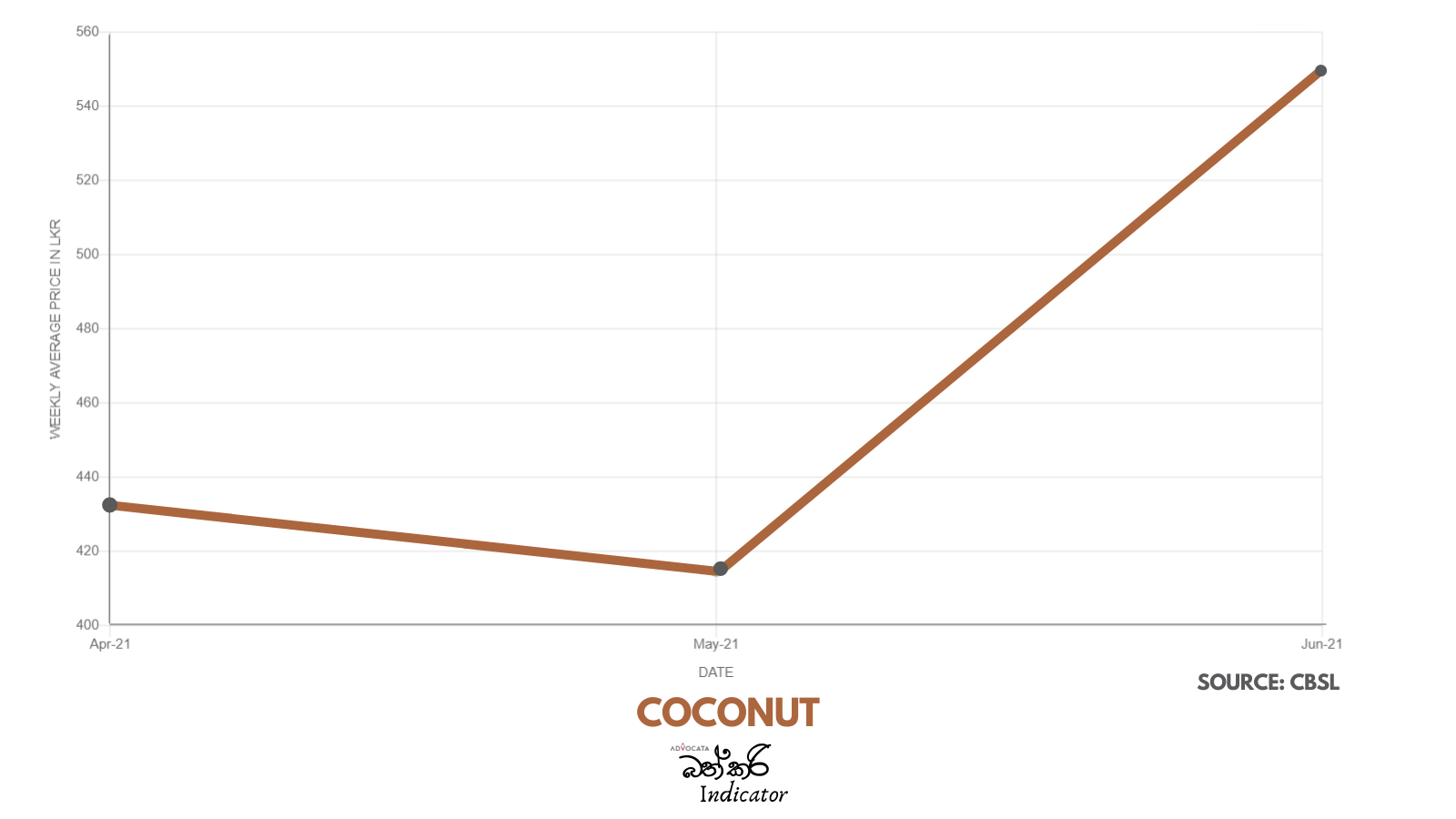
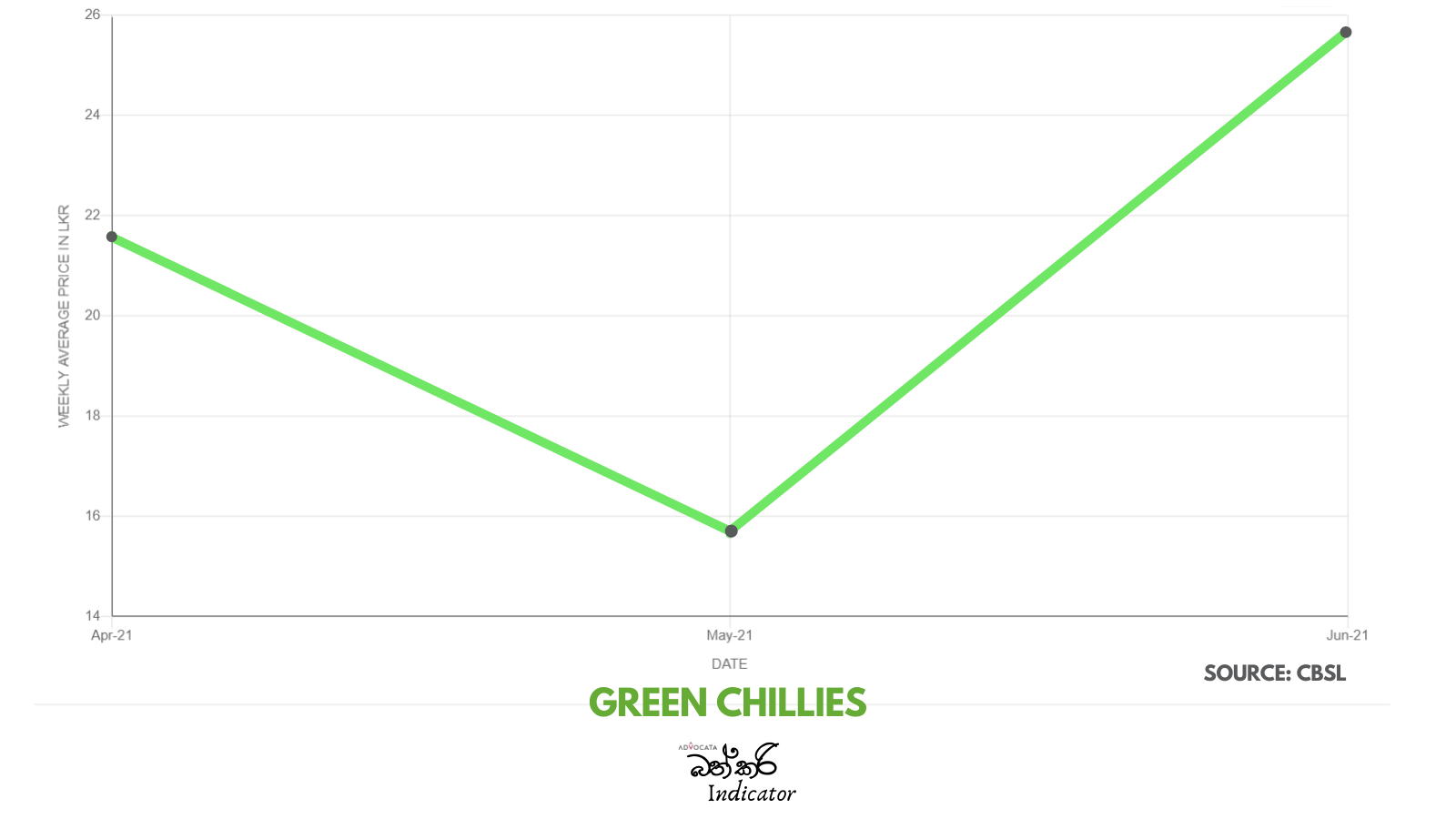
There is serious concern with the steep rise in the price of essentials which has taken place over the past two years. Advocata’s Bath Curry Indicator (BCI), which tracks commonly consumed items, shows a 30% increase in retail food prices in August 2021 compared to August 2020.
The reasons for the increase in prices include import restrictions and tariffs that have disrupted markets. The classic example is turmeric that retailed at Rs.650 per kg prior to the import ban but now retails at Rs 3500 per kg according to the DCS and at around Rs 4400 to Rs6900 on online retailers . Other products are similarly affected.
The recent ban on fertiliser is likely to result in even further increases in the prices of vegetables and cereals over the forthcoming harvests.
These restrictive policies have been compounded by the acute shortage of foreign currency caused by the on-going balance of payments (BOP) crisis. Lack of foreign exchange has imposed additional restrictions on imports resulting in shortages causing prices to spike.
While the increases in prices is a real concern, the causes are complex and are largely due to poor policies.
The balance of payments crisis arises not due to trade policy but due to the levels of aggregate demand in the economy, principally through consumption and investment influenced by the prevailing fiscal and monetary policy. The tax cuts towards the end of 2019, fiscal dominance of monetary policy and non-pass through of global commodity prices through price controls and administered prices have contributed towards excess import demand.
This is evident in the trade data: despite the stringent import restrictions imposed after April 2020, import demand for the six months to June 2021 have surged by 30% over the same period in 2020. While exports in the period have also risen, it is the rapid rise in imports that have caused the negative trade balance.
Price controls and administered prices have led to shortages and hoarding.
Instead of addressing the problem at the root, the government is trying to control the symptoms. Previous attempts at price controls have not succeeded as Advocata’s research in 2018 has shown but better enforcement is not the solution. Instead, the Government should address the policy weaknesses that are the cause of the problem.
Trying to negate policy missteps in fiscal and monetary policy through trade policy in an untenable exercise for it impacts economic efficiency hence growth and productivity and also leads to issues with economic distribution.
Harsh enforcement of price controls could in turn create black markets resulting in significant welfare losses in the form of a deterioration in product quality, elevate scarcities, disadvantaging the poor who are less sophisticated and in the long run lead to higher prices, lower output due to lower investment.
We urge policy makers to urgently address the root cause of the current crisis by increasing tax revenues via more progressive tax policies - by increasing the tax base for both direct and indirect taxes and reducing the tax gap through greater tax effort. Further, it is best where possible to use well targeted cash transfers to vulnerable segments of the population to improve affordability instead of cutting taxing, imposing price control or using administered prices on utilities.
Key Points
Advocata Institute highlights the negative effects of harsh price controls.
The root causes of the present crisis lies in loose monetary and fiscal policies compounded by import controls and exchange control restrictions. Therefore restoring macroeconomic stability is a priority.
Cash transfers to vulnerable segments is a better mechanism to implement distributive policies rather than intervening in market prices through tax subsidies, price controls or administered prices.