The past few months have witnessed rapid currency depreciation across Asia, causing a significant amount of concern across economic sectors. What are the reasons behind these changes, what is their real impact on Asian economies and its people? A panel discussion by Dr. Ross McCleod, Dr. Cris Lingle and Dr. Ajay Shah; moderated by Murtaza Jafferjee at the Asia Liberty Forum, 2019.
Ailing rupee and Price Controls may lead to a shortage of Milk Powder
A cup of tea is every Sri Lankan’s morning mantra. This might not be the case much longer as Sri Lanka may face a shortage of milk powder as several leading milk powder importers are reported to have taken a collective decision to suspend imports. The recent depreciation of the rupee has caused a significant increase in import costs and importers say they are now unable to sell at the controlled price, hence the decision to suspend imports. The same impact will be felt in other industries subject to price controls. The pharmaceutical industry withdrew eleven drugs from the market citing similar reasons.
The currency has depreciated by 10% in the past two months and over 20% in the past year, which will raise landed costs of import products significantly. Importers of goods subject to price controls will continue to be squeezed as their price margins reduce and this will eventually lead to a halt in imports, like in the evident case of milk powder.
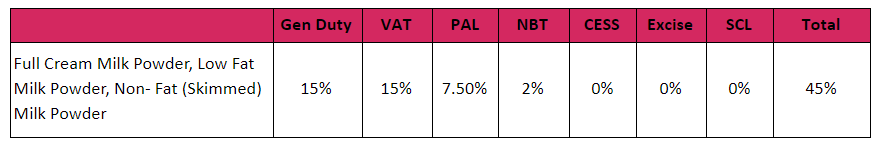
Imported milk powder is taxed at a total of 45% in Sri Lanka, with the objective of protecting local farmers and achieving self-sufficiency in milk products. Despite this self-sufficiency goal, local production meets below 40% of the total domestic milk requirement, considerably below 80% levels in the 1970s. Therefore, majority of the demand in milk products is met through imports, mostly from New Zealand and Australia. Over the last decade, in 7 out of 10 years, imports of milk powder has grown at a higher pace than the growth in local production.
Additionally, in May 2018, changes to existing Price Controls on Milk Prices have raised the controlled price for milk powder to Rs. 345/400g pack and Rs. 860/1kg pack. This price control was enforced by the Consumer Affairs Authority, despite a rise in the global prices of milk. Global milk powder prices fell in 2015 and 2016 and climbed in 2017 and 2018 and now the cost of one metric ton of milk powder in the world market is US$ 3250-3350.
Furthermore, the depreciating rupee, now valued at Rs. 184 to a dollar has only continued to worsen the situation, making it more expensive to import milk powder. “Importers of milk powder are squeezed between the tax (which raises costs), the controlled price which sets a ceiling at which the product retails, and now the depreciating rupee which further raises import costs” says Ravi Ratnasabapathy, Resident Fellow of the Advocata Institute.
The floor price encourages production which the market is sometimes unable to absorb, leading to gluts which cannot be converted to powder (the only long term storage form of milk) due to the controlled price.
A recent report by the Advocata Institute, Price Controls in Sri Lanka, emphasizes the contradictory trajectory of policies in the dairy industry. This tangle of taxes and controls comes at a cost to consumers. Our costs are increasingly becoming apparent by visible shortages of milk powder in the market.
Key Recommendations
High import taxes lead to massive costs for milk powder importers. Changing this would not only mean cheaper milk for consumers, but also cheaper raw materials for downstream processors such as the biscuit or confectionery industry.
The removal of the Maximum Retail Price would allow for a higher level of healthy competition among both importers and local dairy manufacturers, allowing market forces to decide prices.
It is necessary that the government recognises that given the several supply constraints, the objective of self sufficiency is not realistically attainable in the Sri Lankan context. Thus, authorities should recognise the importance if imports in meeting demands of consumers and implement well-thought out measures to level the playing field between importers and domestic producers.
Dhananath Fernando on the depreciating LKR
Advocata Chief Operating Officer, Dhananath Fernando joined the Hot Seat to discuss Sri Lanka’s rapidly depreciating rupee and how the short-sighted policy of cutting down imports will only eventually lead to lower export.